Wednesday, 21 October 2015
Week 7 : Plant Hormone
For the final week of reflective journal on week 7, I learn about the plant hormones. In my opinion, for the 7 weeks that I have been doing reflective journal, I think it is a great idea because it enhance myself to understand the topics that I learnt even more, Furthermore, we do the reflective journal by using blog. As you know, in technology era where the information is spread faster, many people can read through my blog and gain knowledge about the informations that I've shared in my blog.The most frequent sources that I've been refer to is lecture note and also Campbell 10th edition in order to make me understand before I begin to share about the topic that I have learn.
Wednesday, 14 October 2015
Week 6 : Totipotency and Pollination & Development of Plant Embryo
TOTIPOTENCY
ability of a individual plant cell/tissue/organ to regenerate into a whole plant under right condition.
POLLINATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF PLANT EMBRYO
Another topic that I learn in that week is pollination and development of plant embryo. I learn about plants reproductive organs, life cycle of angiosperms, double fertilizations and plant embryogenesis (zygotic & somatic embryogenesis). This is an interesting topic because I learn new things which are zygotic and somatic embryogenesis.
Plants reproductive organs
Female
Ovule that contain megasporongium -> megaspores -> give rise to female gametophytes
Male
Anther has microsporangium ->microspores -> pollen grain (contain male gametophytes)
Life cycle of angiosperms
Double Fertilization
Pollination : transfer of pollen to the part of a seed plant containing the ovule
When pollen grain at anther transfer to the stigma, pollen grain will germinates and give rise to pollen tube that discharges 2 sperms into female gametophyte within the ovule. One sperm nucleus fertilizes egg and generate a 2n diploid zygote.Meanwhile, another sperm nucleus fertilizes a polar cell with two 1n nuclei generating a 3n triploid endosperm that provide nutrients to the developing embryo
Plant embryogenesis
Plant embryogenesis : process that produces a plant embryo from a fertillised ovule by asymmetric cell division and differentiation of undifferentiated cells into tissues and organs
1) Zygotic embryogenesis
Plant embryogenesis : process that produces a plant embryo from a fertillised ovule by asymmetric cell division and differentiation of undifferentiated cells into tissues and organs
1) Zygotic embryogenesis
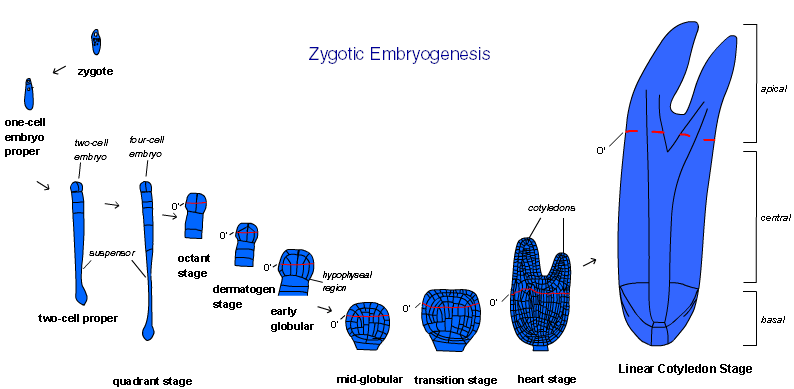
2) Somatic embryogenesis
Tuesday, 6 October 2015
Week 5 : Endosymbiosis and Cell Cycle
ENDOSYMBIOSIS

On week 5, I learn about endosymbiosis and also cell cycle. In endosymbiosis, I can know about the endosymbiosis theory which is a new thing for me and also about mitochondria and chloroplast. There is also an evidence of endosymbiosis regarding mitochondria and chloroplast.
Endosymbiosis Theory :
Evidence for Endosymbiosis :
CELL CYCLE

The Cell Cycle :
Ordered set of events, resulting in cell growth and division into two daughter cells.
-> Multicellular cell is divide to replace lost or damage tissues and allow organisms to grow. Unicellular cell divide is to reproduce
Regulation of cell cycle :

Passage of cell through cell cycle is controlled by proteins in cytoplasm (cyclin)
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
The level of cell cycle become fluctuated with the activation of cyclin that is bind to the Cdks. Cdks will undergo phosphorylation that will add phosphate group to the protein substrates that control process in cell cycle.

On week 5, I learn about endosymbiosis and also cell cycle. In endosymbiosis, I can know about the endosymbiosis theory which is a new thing for me and also about mitochondria and chloroplast. There is also an evidence of endosymbiosis regarding mitochondria and chloroplast.
Endosymbiosis Theory :
- Eukaryotes is derived from prokaryotes
- Heterotrophic baecteria became mitochondria
- Cyanobacteria became chloroplast
- Host cell is a large eukaryotic cell
Evidence for Endosymbiosis :
- Both mitochondria and chloroplast are naturally from prokaryotes. This is because the organelles has circular DNA that does nothave introns (non coding protein) or histone whereas the eukaryotes have linear DNA and associated with histone proteins.
- The organelles also divide by binary fission which splits the cell into two.
- The organelles is a membrane bound organelle which has inner membrane and outer membrane. The inner membrane resemble prokaryotes while the outer membrane resemble eukaryotes.
CELL CYCLE
Next topic is I learnt about the cell cycle which I already know since in my secondary school. But, what makes this topic interesting is, there is cyclin that control the cell cycle and also Cdks which is a new topic for me.
Ordered set of events, resulting in cell growth and division into two daughter cells.
-> Multicellular cell is divide to replace lost or damage tissues and allow organisms to grow. Unicellular cell divide is to reproduce
Regulation of cell cycle :
Passage of cell through cell cycle is controlled by proteins in cytoplasm (cyclin)
- G1 cyclin (D cyclin)
- S-phase cyclin (cyclin A)
- Mitotic cyclin (B cyclin)
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
The level of cell cycle become fluctuated with the activation of cyclin that is bind to the Cdks. Cdks will undergo phosphorylation that will add phosphate group to the protein substrates that control process in cell cycle.
- G1 Cdk (Cdk A)
- S-phase Cdk (Cdk B)
- M-phase Cdk (Cdk b)
Week 4 : Cell Theory, Prokaryotes, Virus, Prions and Viroids
On week 4, I learn about the cell theory, prokaryotes, virus, prions and viroids. there are 3 basic cell theory which are all living organisms are made up of one or more cells, cell is derived from pre-existing cell by cell division and cell is the basic unit of structure & function in living organisms.There are addition of 3 for modern cell theory.
PROKARYOTES

In prokaryotes it has cell wall, capsule, cell membrane, nucleoid region (DNA), flagella and pili
VIRUS
-has genetic material (DNA & RNA)
-reproduce inside host cell
-nucleic acid surrounded by protective protein coat called capsid
some virus surrounded by outer membrane layer called an envelope made up of lipid and protein.
-Virus reproduce in 2 ways :
1) Lytic Cycle 2) Lysogeny Cycle
PRIONS
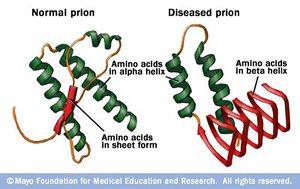
-an infectious agent
-specific protein that prion was composed is Prion Protein (PrP)
-PrP found in infectious material
VIROIDS
-small circular RNA without protein coat
-contain 20 nucleotides
-infect plants
Week 3 : History of Life
ORIGIN OF LIFE
4 requirements must have existed:
- Little/no free oxygen-earth's early atmosphere was strongly reducing.
- Source of energy to form organic molecules-early earth was a place of high energy
- Availability of chemical building blocks such as CO2, N2, H2, CO, water vapour. Some NH3, H2S and CH4,little or no O2.
- Sufficient time for molecule to accumulate and react
The first prokaryote that I learnt is chemoautotrophs that consume organic molecules for both energy and carbon and the first autotrophs that I have learnt is photoautotrophs. It used light electron from H2O to fix CO2 into sugar. It is happen when the organic compounds from the ocean become depleted, the prokaryotes who able to make their own food can grow (autotrophs)
As for the topics for week 3-5, I already published a week 4 topic but I republished topic in week 4 or organize my blog so all 3 weeks topic share the same date.
Week 2 : Selection in Action & SCL activities
On week 2, I learn about the topic of selection in action and SCL activities. The topic of selection in action, I learn about the concept and examples of natural and artificial selection where natural selection is a process in which
individuals have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce
at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits. For example,
Finches evolved with different type of beak. Meanwhile, artificial selection is the selective breeding of domesticated plants & animals to encourage the occurrence of desireable traits. For example, Cat breeding. Cat breed to get a desireable traits.
Finches evolved with different type of beak. Meanwhile, artificial selection is the selective breeding of domesticated plants & animals to encourage the occurrence of desireable traits. For example, Cat breeding. Cat breed to get a desireable traits.
Variation : Refers to an individual that possesses characteristics different from each other
Example include tortoise : Intermediate, doomed (in wet areas, lots of mosses) and sealed shell
Example include finches : Finches evolved to different size and type of beak.
Adaptation : Process of change by which an organism/species becomes better suited to its environment
Fossil evidence : Coral formation, volcanic island
KEY TO INSIGHTS LED TO DARWIN'S THEORY
Artificial selection : The selective breeding of domestical plants & animals to encourage the occurance of desireable traits
Heretibility : Ability of traits to be inherited from one generation to one generation.
Struggle for survival : This fittest one who would survive
4 MAIN PRINCIPLES OF NATURAL SELECTION
-Variation : Refers to an individual that possesses characteristics different from each other
-Overproduction : Ability of species to produce far more offspring than can possibly survive.
-Adaptation :
provides the basis for the population to adapt to environmental changes, such as the volcanic eruption on the island
-Descent with modification : Pass down adaptation from one generation to one generation
MODERN SYNTHESIS OF EVOLUTIONARY THEORY
DNA sequence analysis
- process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within DNA molecules
Pseudogenes
- non functional sequence of genomic DNA originally derived from functional genes
Homeobox genes
- a large family of similar genes that direct the formation of many body structures during early embryonic development
Protein Comparisons
- different organisms have different protein sequence
I have been introduced to reflective journal on week 2 but I start it a bit late because of holidays and does not have internet connection at my village.
Thursday, 1 October 2015
Week 1 : Historical Development of Theory of Evolution
Ideas on Evolution Prior to Darwin
ARISTOTLE (384-322)
- Arrange organisms from simple to complex.
- Visualized as not perfect but move to perfectness.
JEAN BAPTISTE LAMARK (1744-1829)
- French naturalist.
- Evolution occur by inheritance of acquired characteristics.
- Organisms subjected to a external force
- Theory : Evolution of modern giraffe.
CHARLES LYELL
- Book : 'Principles of Geology'
- Earth must be very old
- Subjected to natural processes in past just like present time
- Erosion, earthquakes, volcanoes
- Idea lead Charles Darwin to understand biological evolution.
- All species of life have evolved over time from common ancestors through natural selection.
- The long neck of giraffe due to mutation, variation.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)


